How hearing aids work?
Hearing aids are devices that are placed in the ears to improve the quality of sound perceived by people with hearing problems. This hearing solution is indicated for people suffering from hearing loss or hearing difficulties in certain circumstances.
When wearing hearing aids, external sounds are picked up through the microphone and processed to match the person’s hearing patterns. The processed sound is transmitted through the speakers of the hearing aids and is perceived by the wearer clearer and easier to understand.
Which are the right hearing aids for me?
There are several types of hearing aids available in the market, each with its features and benefits.
The type of hearing aid that is best for you depends on your individual needs and the recommendations of your audiologist or hearing healthcare specialist. Some of the most common types of hearing aids are:
Types of hearing aids
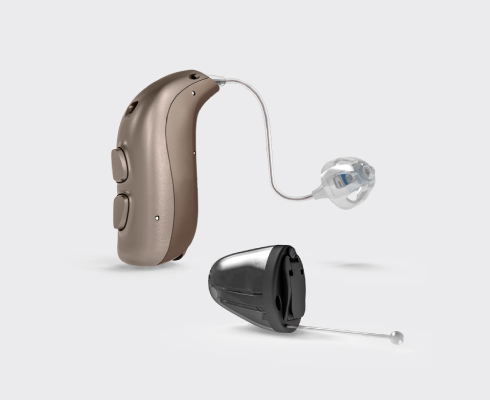






In-The-Ear hearing aids
In-The-Ear hearing aids are the ones that stand out for their ability to be almost invisible.
Being inside the ear canal, they are the most discreet and small hearing aids, they are almost invisible.
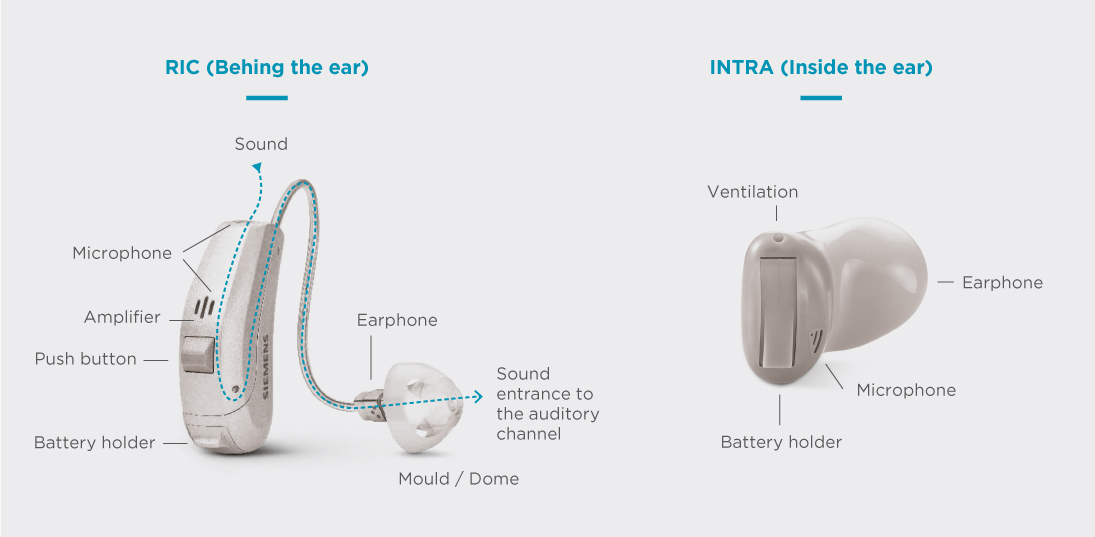
RIC (Receiver-In-Canal) or RITE hearing aids
Hearing aids RIC (Receiver-In-Canal) or RITE are hearing aids with a receiver that is placed inside the ear, in the ear canal.
They provide great sound quality and are also lighter and more comfortable to wear than traditional hearing aids.
They are available in different colours to perfectly suit your skin or hair tone.

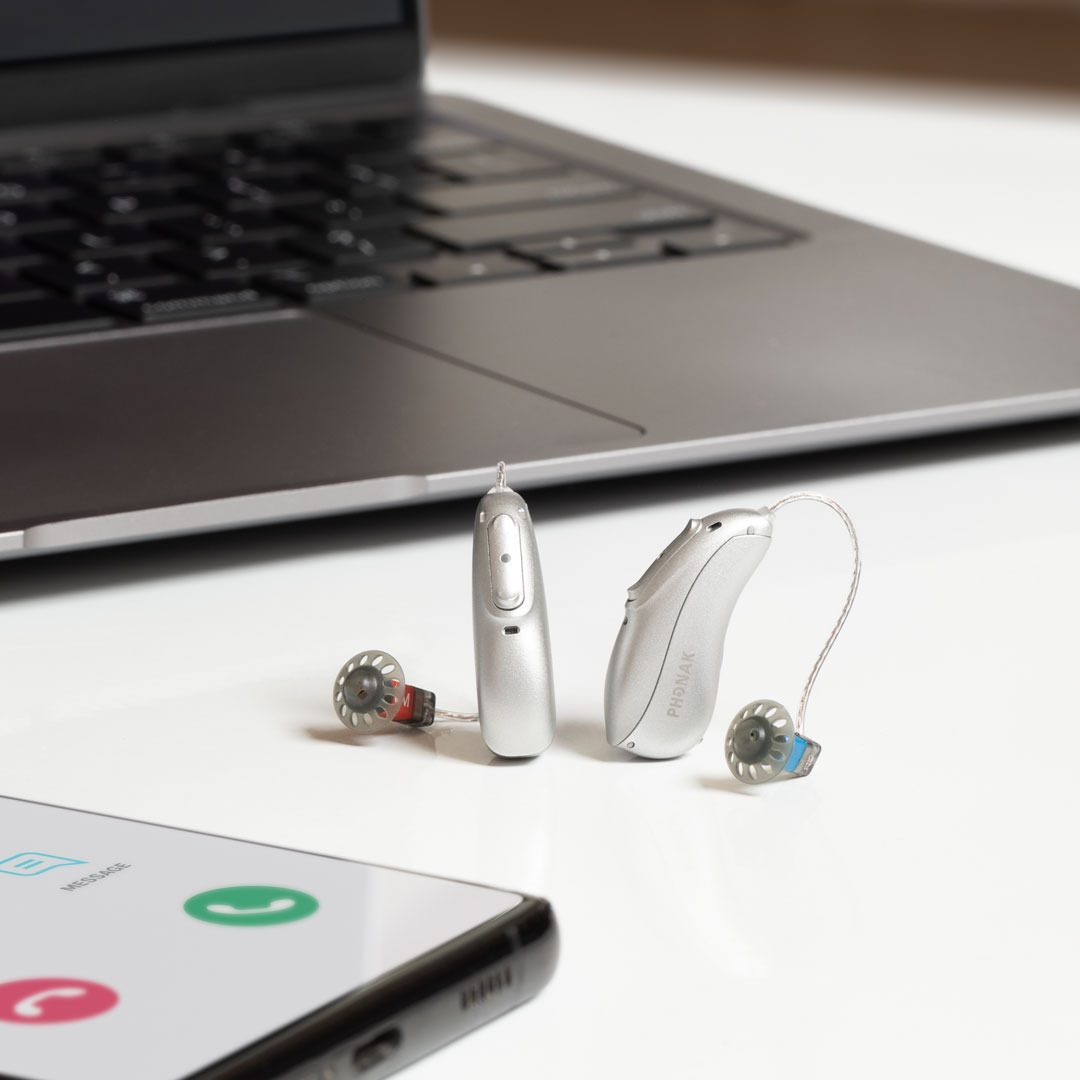
Hearing aids connected to the TV (or other audio equipment) and the mobile phone
Connected hearing aids are those that, as the name suggests, are characterized by being able to connect to the television (or other audio equipment) or the mobile phone to improve listening.
Also, those hearing aids with Bluetooth connectivity can connect your hearing aid to any device that has Bluetooth, such as your TV or phone.
There are also hearing aids with radio frequency (RF), which can be connected to the television or to the phone using a radio frequency transmission, which allows them to hear the sounds with very high quality.

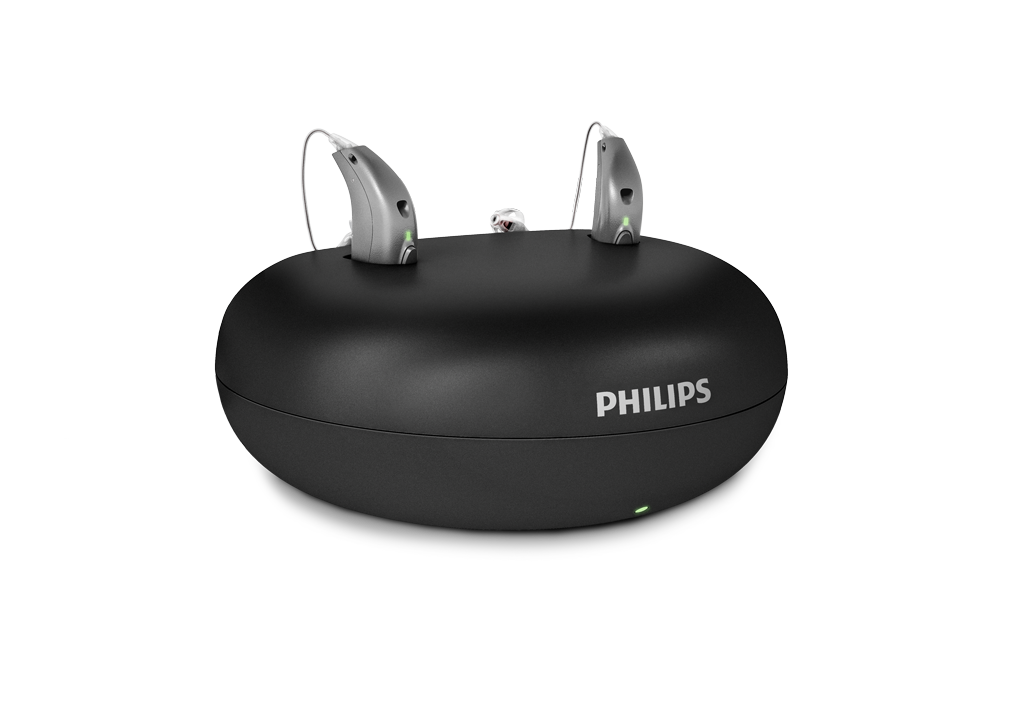
Battery-free hearing aids or rechargeable
Battery-free hearing aids, also called rechargeable hearing aids, are an increasingly popular option for those with hearing loss. These types of hearing aids work with rechargeable batteries instead of batteries.
The great advantage of rechargeable hearing aids is that you do not need to change the batteries constantly, as they have a much longer battery duration and are therefore very comfortable and practical hearing aids.

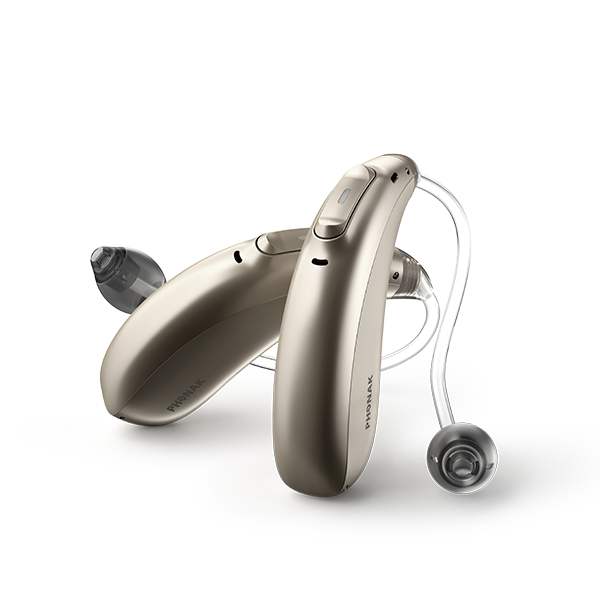
Behind the ear hearing aids
Behind-the-ear hearing aids are a type of hearing aid that is placed outside the ear, behind the ear.
This is a more visible type of hearing aid than in-the-ear hearing aids, but they are very comfortable to wear, more powerful and resistant. In addition, they also provide very good sound quality.
Depending on the hearing loss, they can be adapted with a thin tube for more discretion (open fit).

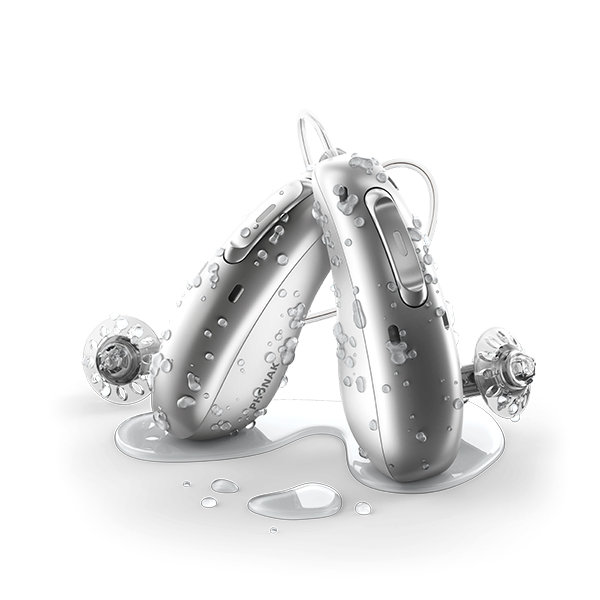
Hearing aids resistant to water and other environmental elements
Water-resistant hearing aids are a type of hearing aid that withstands exposure to water and other environmental elements. They are very useful for people who practice water sports (they can submerge up to half a meter deep), or those who live in places with wet and rainy weather or who sweat a lot, as they allow them to use their hearing aids without having to worry about them getting wet and damaged.
There are different types of water-resistant hearing aids, all of which are designed to withstand direct exposure to water and other environmental elements, such as dust and sweat, either because they are built with water-resistant materials or because they have a special coating that protects them from water.
How hearing aids work step by step
Hearing aids are not simply amplification devices, but very sophisticated devices that are dedicated to increasing the intensity of sound and enabling the user’s communication and listening.
They are designed to stimulate the ear in order to prevent hearing impairment and ensure the understanding of the speaker.
Below, we describe in detail how headphones work:
- Microphones pick up sounds.
- The processor chip analyses the sounds.
- The processed sound is sent to the amplifier.
- The amplified sound is sent to the speaker.
- The speaker transmits the sounds to the inner ear.
- In the inner ear, sounds are transformed into electrical impulses.
- The brain collects the impulses and processes them.
Parts of a hearing aid
All hearing aids have five basic components: microphone (receiver of sound), amplifier, earpiece, speaker (emitter of sound), battery (with battery holder) and a computer chip – programmed according to the individual’s needs.
Hearing aids are composed of three parts: the microphone, the amplifier and the receiver or speaker:
- Microphone: receives the sound waves of the environment sound and converts them into electrical signals
- Amplifier: increases and modulates the strength of electrical audio signals and sends them to the ear, amplifying their intensity.
- Receiver/Speaker: converts the amplified electrical signals into sound and sends it deeper into the ear, reaching the ear canal.
In hearing aid models there may be a difference between the amount of sound captured and the speech understanding. The higher the quality of the hearing aid, the more natural the sound will be, due to the characteristics of bandwidth, automatic volume regulation, noise management and the cancellation of couplings and annoying sounds.
More advanced hearing aids also have a wide range of customization options and can be connected wirelessly to different devices, such as mobile phones.
Hearing aids brands that Audioson works with









